What is JDK, JRE, and JVM?
In order to start programming in Java, we need to make sure all the pre-requisites are fulfilled. The machine must contain a package that provides the environment for software development and execution in Java. This environment is provided by JDK. Let us explore the theoretical aspects of JDK.
What is JDK?
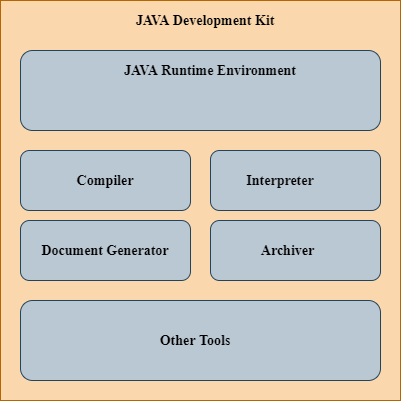
Java Development Kit is commonly known as the JDK. It provides a software development environment for the development and execution of Java-based applications. It has physical existence in the machine. The contents of the JDK are as follows:
- JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
- Compiler (javac)
- Interpreter (java)
- Archiver (jar)
- Documentation Generator (javadoc)
- Other tools necessary for the development
There are three Java platforms released by Oracle. Each of the platforms has a specific utility. They are:
- J2SE (Standard Edition) Platform: It is used for the core and basic implementation of Java, which we will be covering in this lecture.
- J2EE(Enterprise Edition) Platform: It is used for advanced implementation of Java comprising of collections, etc.
- J2ME(Micro Edition) Platform: It is used for android development.
JDK is an implementation of any one of the platforms given above.
What is JRE?
Java Runtime Environment is commonly known as JRE. It is a part of JDK and has its utility in providing the run time environment only. It has no role in the development of the Java program/application. It provides a minimum requirement for the execution of a Java program to be successful. It comprises of many libraries and toolkits with their dedicated utility in user Interface( Abstract Window Toolkit), Integration(Java Database Connectivity), Other Base Libraries(Java Management Extensions), and Deployment( Java Web Start). One of the most important members of JRE is JVM(Java Virtual Machine).
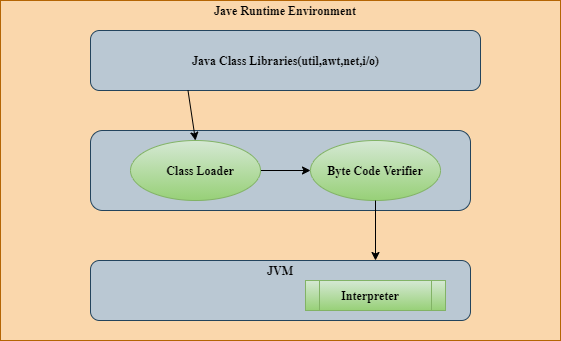
Let us look at the basic flow of JRE in the execution of Java Program.
- Upon saving our java program(extension
.java) , the compiler(javac) creates the byte code(extension.class). - All the pre-requisite classes are loaded, which is mentioned to be required for execution. This step is performed by Class Loader.
- Java is a robust and secure language that always checks the format of byte code to avoid the execution of illegal codes. This step is performed by Byte Code Verifier. It makes sure that JVM specification is strictly adhered to.
- The bytecode is then loaded and executed by the interpreter by valid calls to the underlying hardware.
What is JVM?
JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine. It is a virtual machine and doesn't exist physically. It is a specification that provides a runtime environment. Regardless of the java program, it is JVM which is responsible to execute the byte code line by line. The main tasks of JVM include loading, verifying, executing, and providing the execution environment.
There are three notions of JVM. They are:
- Specification:
- It is where the working of Java Virtual Machine is specified. The implementation is usually provided by the parent company and they are free to choose the algorithm.
- Implementation:
- It is a computer program that makes sure, JVM specification is met.
- Runtime Instance:
- Whenever a command is made to execute a java class, an instance of JVM is created. JVM becomes the instance of JRE.
- In the next lesson, we will learn to install JDK and perform the environment setup.

