React CSS
There are two ways to style in React, inline styling, and CSS stylesheet.
Inline styling:
Inline styles must be passed to attribute as a javascript object, and since javascript expressions are placed in {} brackets. The style attribute ends up with two curly brackets.
import React from "react";
const App = () => {
return(
<>
<p style={{color: "red"}}>I am a red paragraph.</p>
</>
)
}
export default App
Result:
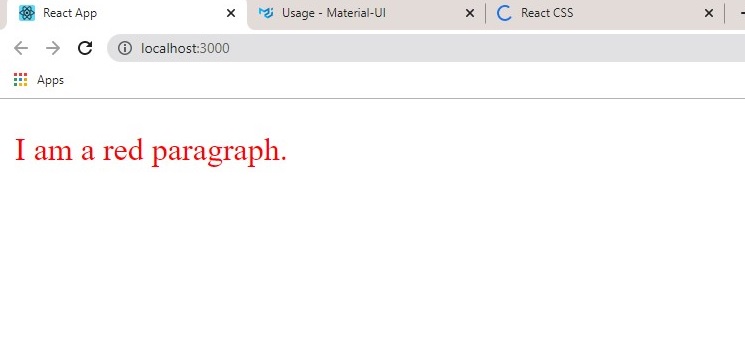
Remember, style property names must be written in camel Case e.g. padding-bottom is written as padding-bottom.
CSS Stylesheets:
Write your CSS styling in a different file e.g. styles.css then import it into your .js file:
Styles.css:
p {
color: cornflowerblue;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
h1 {
color: blue;
}
App.js:
import React from "react";
import './styles.css'
const App = () => {
return(
<>
<h1>Hello,</h1>
<p style={{color: "red"}}>I am a red paragraph.</p>
</>
)
}
export default App
Result:
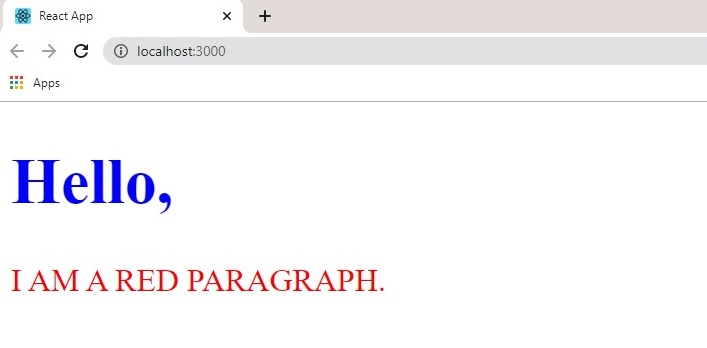
Another way of adding styling to your application is to use modules. CSS modules are convenient for components placed in separate files.
Example:
Let’s make a top navigation header in React. In App.js, we write:
import React from 'react'
import './styles.css'
function App() {
return(
<div className='App'>
<ul>
<li><a href='#'>Home</a></li>
<li><a href='#'>About</a></li>
<li><a href='#'>Orders</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
export default App
We import a styles.css file already created.
The styles.css file looks thus:
.App {
background-color: #f1f1f1;
margin: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
ul {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
align-items: center;
}
ul li {
list-style-type: none;
}
li a {
text-decoration: none;
}
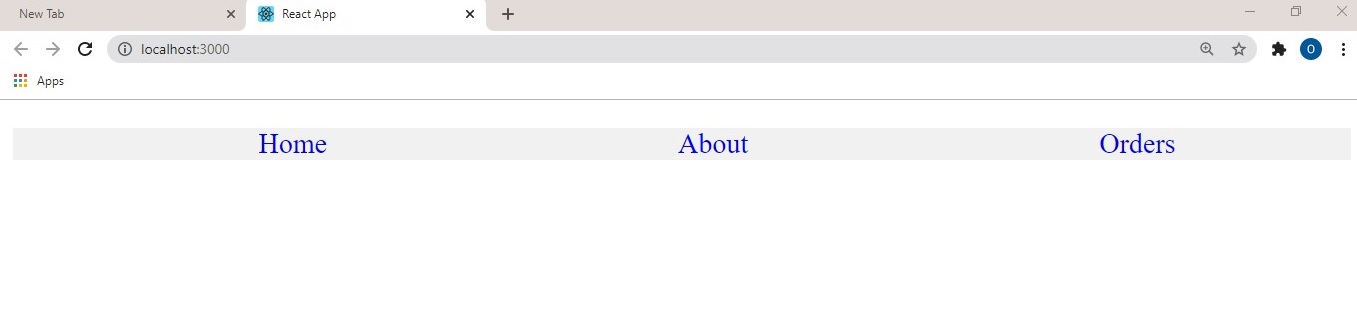
Result:
Don't have an account? Sign up!

