How to Handle Duplicate Records in MySQL?
It can happen that we have redundant data in our tables. This data needs to be handled it can lead to incorrect query results and data mismatches. We will look at the best way to handle duplicates.
Find duplicate records in MySQL
An easy way to detect duplicates in our data is to use a query with the syntax
SELECT <column-name>,COUNT(<column-name>)
FROM <table_name>
GROUP BY <colum-name>
HAVING COUNT(column-name) > 1;
Example:
SELECT first_name, COUNT(first_name)
FROM employees
GROUP BY first_name
HAVING COUNT(first_name) > 1;
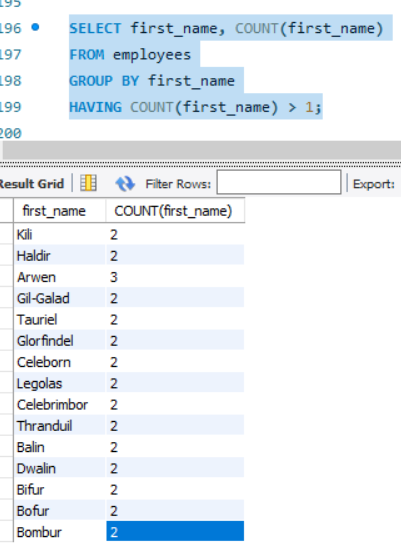
We can extend this to as many columns as we need. We just need to add the count<column_name> > 1 in the having cluase for each of the columns we need.
Delete duplicate records in MySQL
To Delete duplicate records, we can use the delete JOIN statement. The Basic syntax of a Delete Join is
DELETE [target table]
FROM [table1]
INNER JOIN [table2]
ON [table1.[joining column] = [table2].[joining column]
WHERE [condition];
Example:
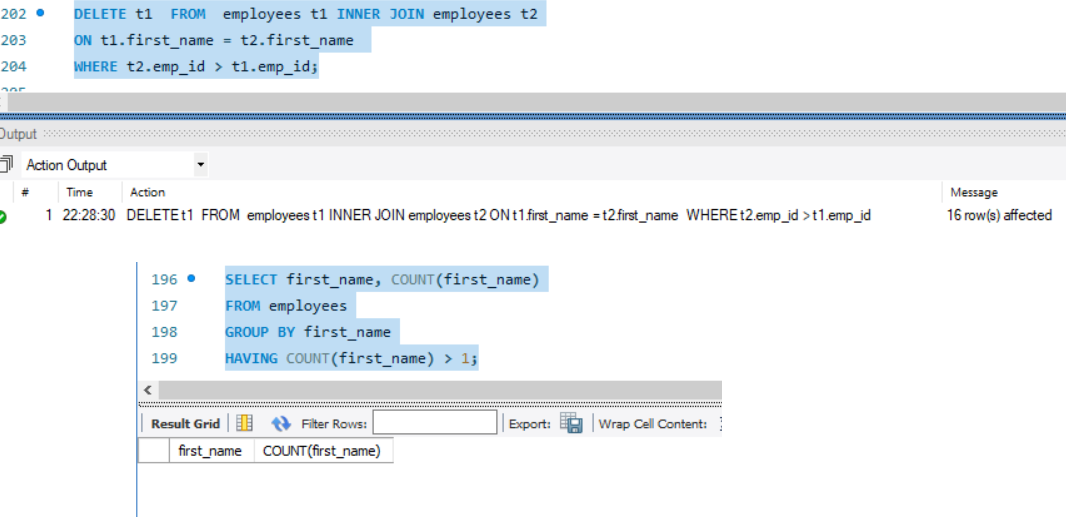
DELETE t1 FROM employees t1 INNER JOIN employees t2
ON t1.first_name = t2.first_name
WHERE t2.emp_id > t1.emp_id;
We can recheck duplicate records using the below Query,
SELECT first_name, COUNT(first_name)
FROM employees
GROUP BY first_name
HAVING COUNT(first_name) > 1;
Don't have an account? Sign up!

