MySQL Wildcards
MySQL Wildcards are used with the LIKE and the NOT LIKE clauses.
MySQL Wildcards syntax
The Basic syntax of using a wildcard is:
expression LIKE pattern [ESCAPE <escape_character>]
There are two wildcards used in MySQL
- The
%wildcard - The
_wildcard
MySQL % wildcard
We use the % operator to match zero or more characters in a string.
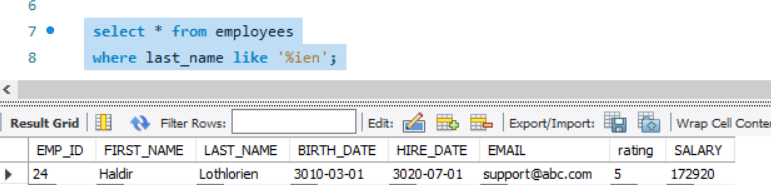
Example1: % followed by a pattern
The example will check if any strings are ending with 'ien'
select * from employees
where last_name like '%ien';
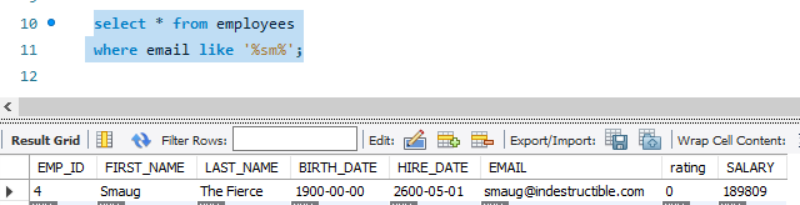
Example 2: %<pattern>%
This example searches for the pattern in between any number of characters.
select * from employees
where email like '%sm%';
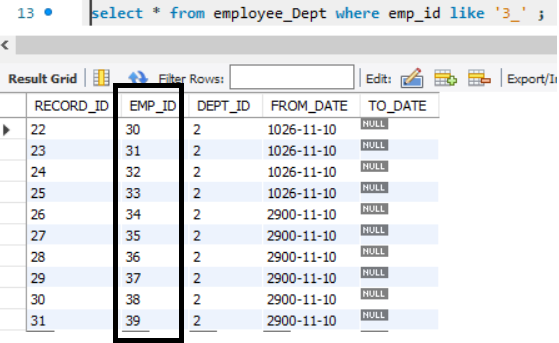
MySQL _ wildcard
We can check for exactly one character with the underscore( _ ) wildcard.
Example:
If we want to check if there are any employees with employee id in the 30s =, we can do
select * from employee_Dept where emp_id like '3_' ;
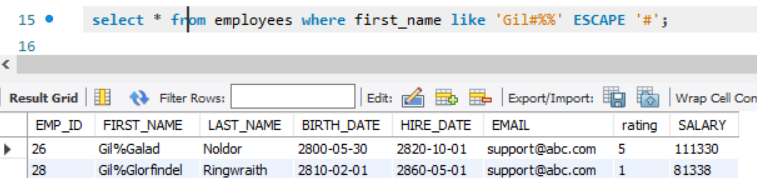
MySQL ESCAPE character
IF we have a pattern containing one of the wildcards, we can introduce a new character and escape it.
select * from employees where first_name like 'Gil#%%' ESCAPE '#';
Here the '#%%' with the Escape character will search for a % in the string.
Don't have an account? Sign up!

