MySQL Stored Procedures and Types with Examples
A stored procedure is a group of SQL statements that have been created and stored in the database. To create stored procedures we use the CREATE Procedures statement. Stored Procedures is the closet we come to making user-defined functions in MySQL.
The Basic syntax for creating a stored procedure,
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE <procedure-name>()
Begin
<procedure-Query>
END$$
DELIMITER $$;
We can have stored procedures with:
- No Parameters
- In Parameter
- Out Parameter
- InOut Parameter
We will see examples of each.
How to create a Stored Procedure in MySQL?
We can create a stored procedure with or without parameters.
Create a Stored procedure with No Parameters in MySQL
An example of a simple stored procedure with no parameters
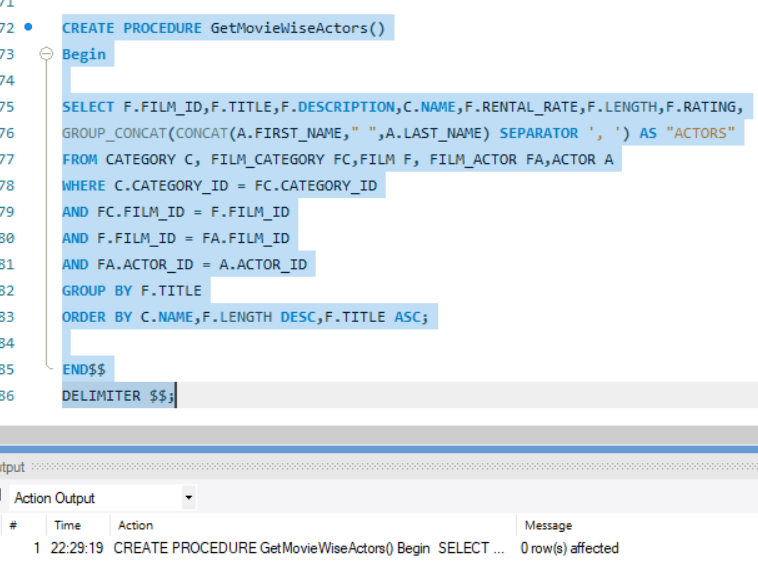
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetMovieWiseActors()
Begin
SELECT F.FILM_ID,F.TITLE,F.DESCRIPTION,C.NAME,F.RENTAL_RATE,F.LENGTH,F.RATING,
GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT(A.FIRST_NAME," ",A.LAST_NAME) SEPARATOR ', ') AS "ACTORS"
FROM CATEGORY C, FILM_CATEGORY FC,FILM F, FILM_ACTOR FA,ACTOR A
WHERE C.CATEGORY_ID = FC.CATEGORY_ID
AND FC.FILM_ID = F.FILM_ID
AND F.FILM_ID = FA.FILM_ID
AND FA.ACTOR_ID = A.ACTOR_ID
GROUP BY F.TITLE
ORDER BY C.NAME,F.LENGTH DESC,F.TITLE ASC;
END$$
DELIMITER $$;
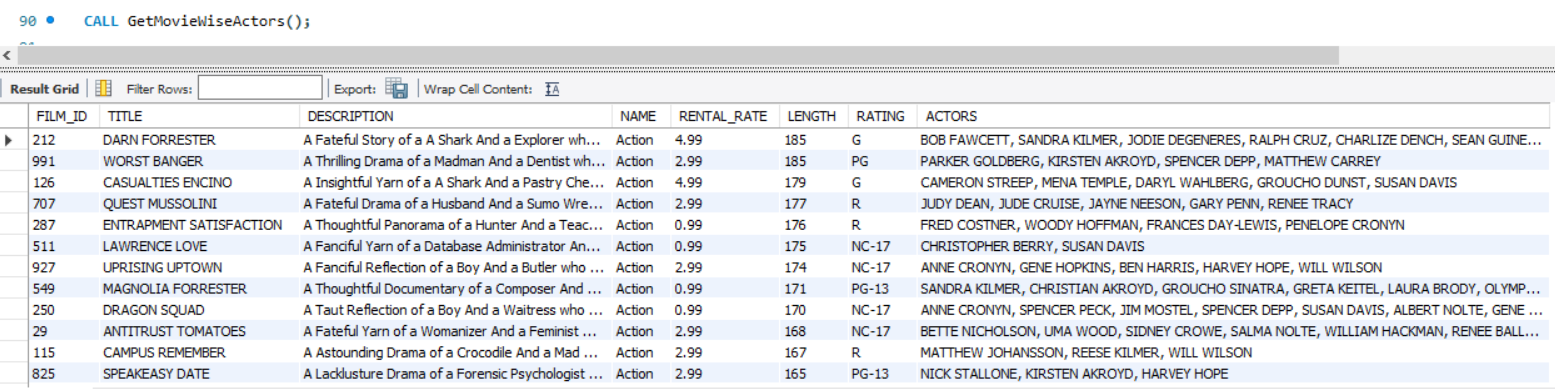
To execute the stored procedure we do:
CALL <procedure-name>();
Example:
CALL GetMovieWiseActors();
Create a Stored procedure with In Parameter in MySQL
We can create stored procedures that take inputs from the caller. These are called as procedures with IN parameters. An example of a simple Procedure is
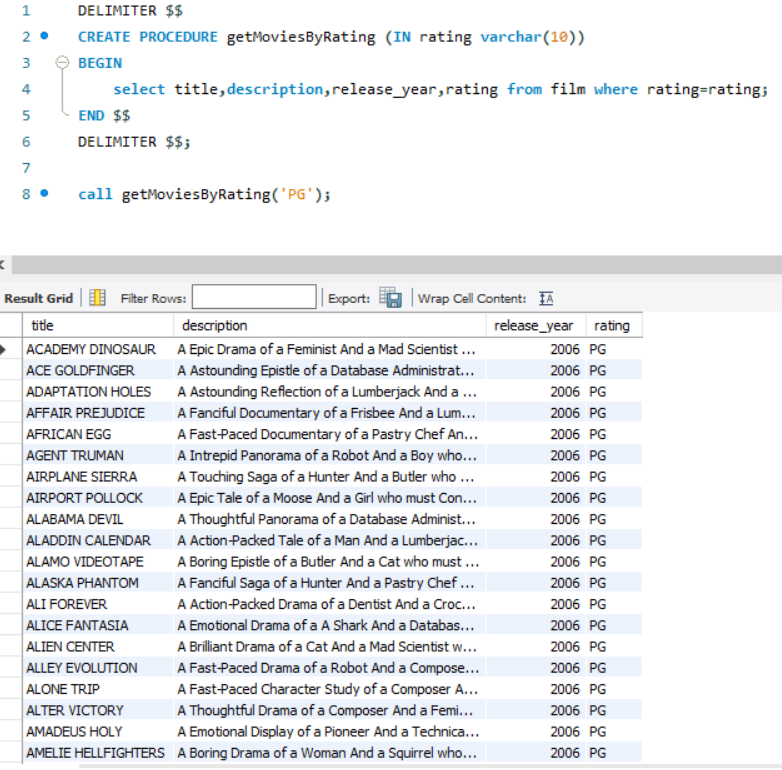
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE getMoviesByRating (IN rating varchar(10))
BEGIN
select title,description,release_year,rating from film where rating=rating;
END $$
DELIMITER $$;
To call the procedure we need to give it an input
call getMoviesByRating('PG');
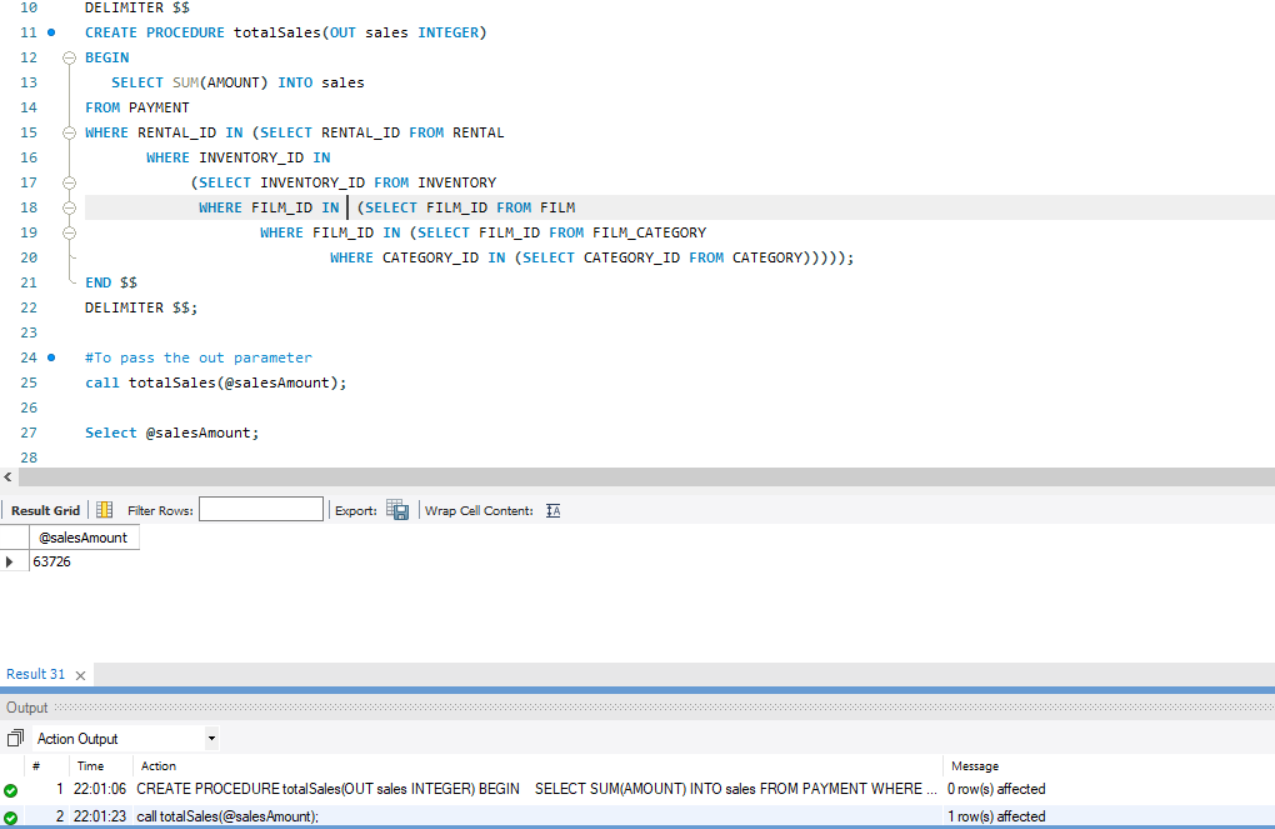
Stored procedures with Out Parameters in MySQL
We can create a procedure to get the output in an out parameter. For a procedure that needs a out parameter, we need to use the Select ... INTO statement. We do that as follows,
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE totalSales(OUT sales INTEGER)
BEGIN
SELECT SUM(AMOUNT) INTO sales
FROM PAYMENT
WHERE RENTAL_ID IN (SELECT RENTAL_ID FROM RENTAL
WHERE INVENTORY_ID IN
(SELECT INVENTORY_ID FROM INVENTORY
WHERE FILM_ID IN
(SELECT FILM_ID FROM FILM
WHERE FILM_ID IN
(SELECT FILM_ID FROM FILM_CATEGORY
WHERE CATEGORY_ID IN
(SELECT CATEGORY_ID FROM CATEGORY)))));
END $$
DELIMITER $$;
To call this procedure we need to supply an out parameter where the values are stored.
call totalSales(@salesAmount);
Create a Stored procedure with INOUT Parameters
A stored procedure can have INOUT parameters. An example of the same is as follows:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE getFullName (INOUT fullNameList varchar(4000))
BEGIN
DECLARE finished INTEGER DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE fullName varchar(100) DEFAULT "";
#Cursor declaration
DEClARE curName
CURSOR FOR
SELECT concat(first_name ,' , ' , last_name) FROM employees LIMIT 10;
#declare NOT FOUND handler
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET finished = 1;
#Open cursor
OPEN curName;
#fetch records
getName: LOOP
FETCH curName INTO fullName;
IF finished = 1 THEN
LEAVE getName;
END IF;
SET fullNameList = CONCAT(fullName,";",fullNameList);
END LOOP getName;
CLOSE curName;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
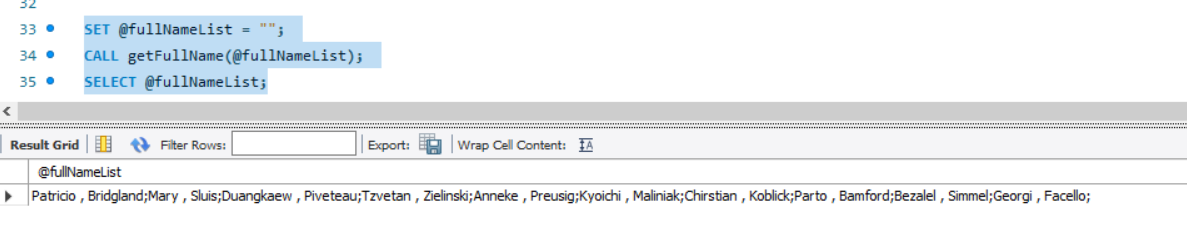
To call this procedure we first need to initialize a session variable and then send it as a parameter. This parameter is then filled in with values using the procedure call and sent out as a Out parameter.
SET @fullNameList = "";
CALL getFullName(@fullNameList);
SELECT @fullNameList;
The way the procedure works is that the first time a procedure is run in MySQL, MySQL caches it in memory. After that every time the stored procedure is run in the same session the results are returned from the cache. We can also pass parameters to the stored procedures exactly like a user-defined function.
Stored Procedures help
- Reuse the commonly used code without redundant code.
- Reduce the hits on the database since the output is stored in the cache.
- Increases security because the underlying tables need not be exposed to all the users, just the stored procedures need to be.
Stored Procedures come at the cost of extra resources because we need to use more cache memory. It is also difficult to troubleshoot or debug stored procedures.
How to Alter stored procedure in MySQL?
As per MySQL, we cannot change the body, input, and output parameters of a Stored Procedure.
This statement can be used to change the characteristics of a stored procedure. More than one change may be specified in an ALTER PROCEDURE statement. However, you cannot change the parameters or body of a stored procedure using this statement; to make such changes, you must drop and re-create the procedure using DROP PROCEDURE and CREATE PROCEDURE.
The options for Altering a Procedure are :
ALTER PROCEDURE proc_name [characteristic ...]
characteristic:
COMMENT 'string'
| LANGUAGE SQL
| { CONTAINS SQL | NO SQL | READS SQL DATA | MODIFIES SQL DATA }
| SQL SECURITY { DEFINER | INVOKER }
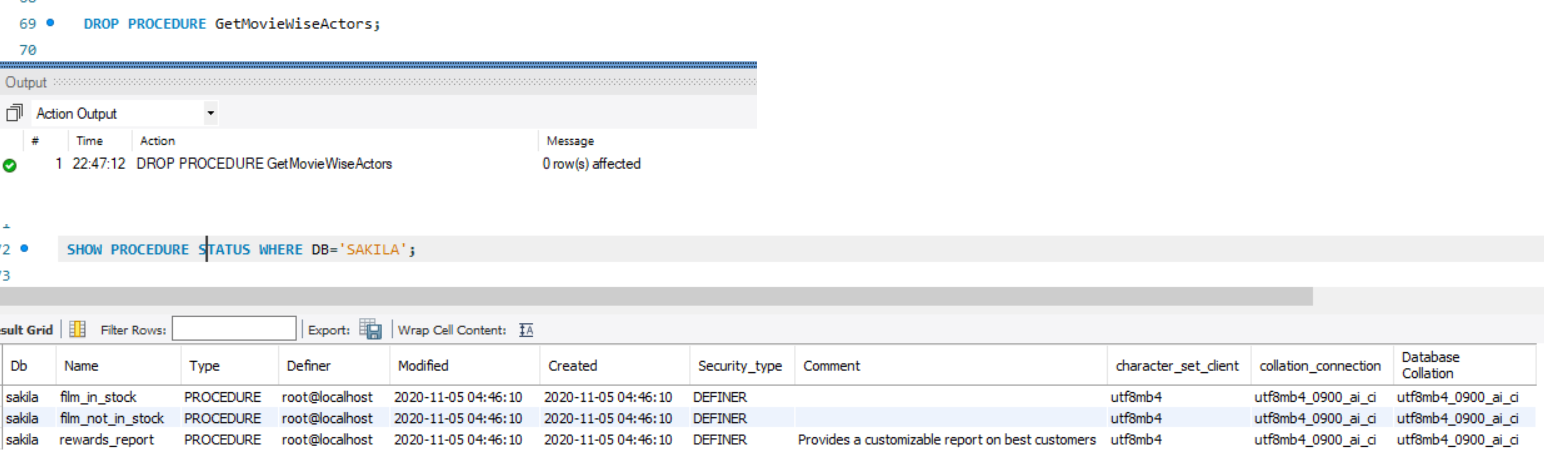
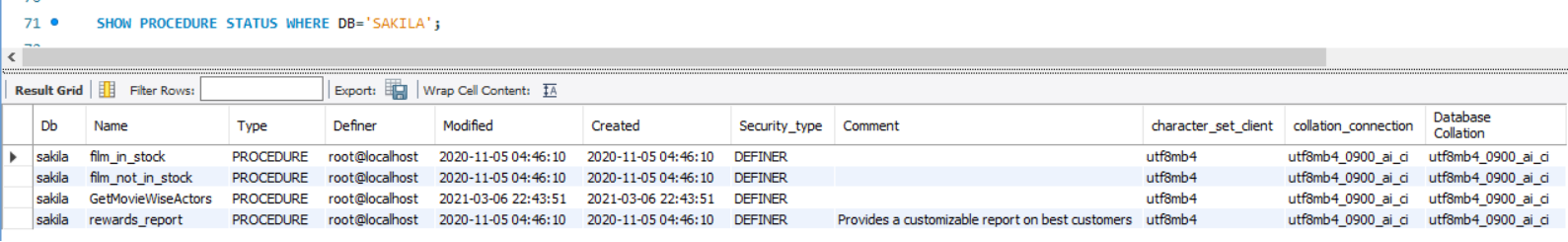
How to show all stored procedures in MySQL?
To get all the stored procedures that are present in a database schema we use the Show procedures statement
SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS
WHERE DB='SAKILA';
How to Remove/Drop a stored procedure in MySQL?
To remove a procedure we use the DROP Procedure statement. The basic syntax is
DROP PROCEDURE [IF EXISTS] stored_procedure_name;
For example
DROP PROCEDURE GetMovieWiseActors;