MySQL View: Create, Update, Drop, Rename View
MySQL View is a virtual table based on the MySQL Statement. The MySQL View is essentially a query that is stored in the database. The View does not physically store the data like a table but stores the query instead.
The advantage of using Views are as follows:
- It avoids repetitions. If we have a query that is used frequently we can just store it as a view instead of formulating and running it over and over again.
- We can hide business logic or complexity by using Views.
- We can also encapsulate sensitive queries in a View and limit exposure, thus increasing security
- A view can be used as a backup for a table when migrating.
Create a View in MySQL
To create a View, we use the Create View Query. The basic syntax is
CREATE [OR REPLACE] VIEW [db_name.]view_name [(column_list)]
AS
select-statement;
For an example of a view,
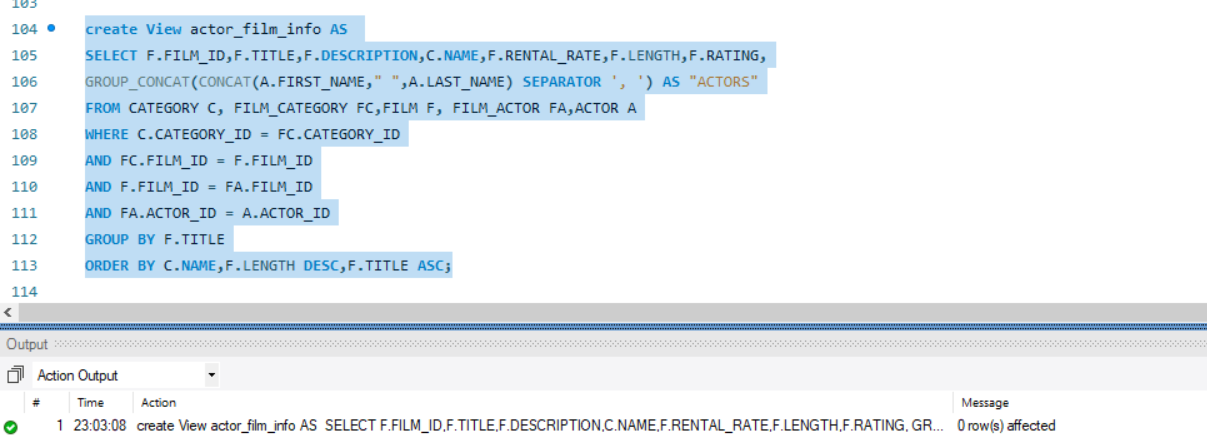
create View actor_film_info AS
SELECT F.FILM_ID,F.TITLE,F.DESCRIPTION,C.NAME,F.RENTAL_RATE,F.LENGTH,F.RATING,
GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT(A.FIRST_NAME," ",A.LAST_NAME) SEPARATOR ', ') AS "ACTORS"
FROM CATEGORY C, FILM_CATEGORY FC,FILM F, FILM_ACTOR FA,ACTOR A
WHERE C.CATEGORY_ID = FC.CATEGORY_ID
AND FC.FILM_ID = F.FILM_ID
AND F.FILM_ID = FA.FILM_ID
AND FA.ACTOR_ID = A.ACTOR_ID
GROUP BY F.TITLE
ORDER BY C.NAME,F.LENGTH DESC,F.TITLE ASC;
To check if the view was created, we can do :
Show FULL Tables;
The view are listed below,
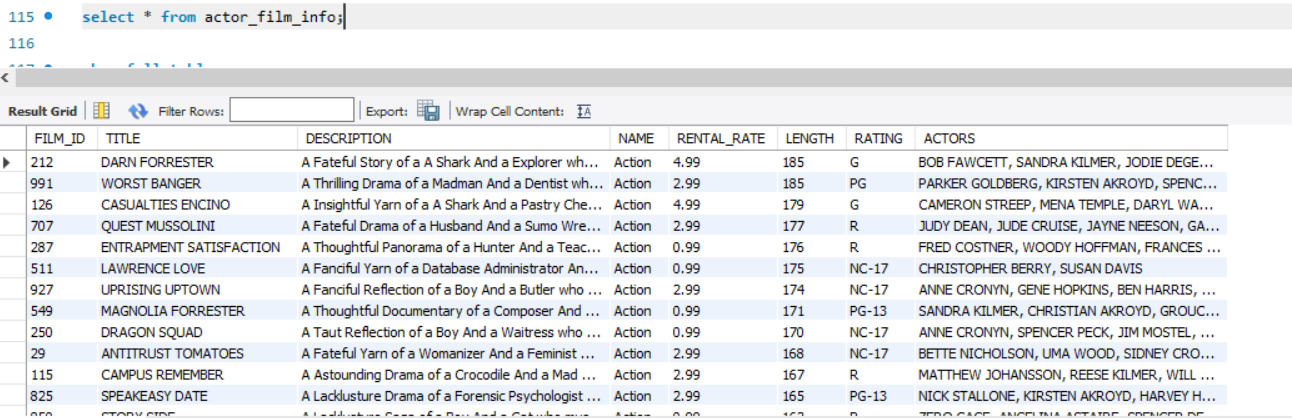
To check the records of the view, we can trigger a select query on it.
select * from actor_film_info;
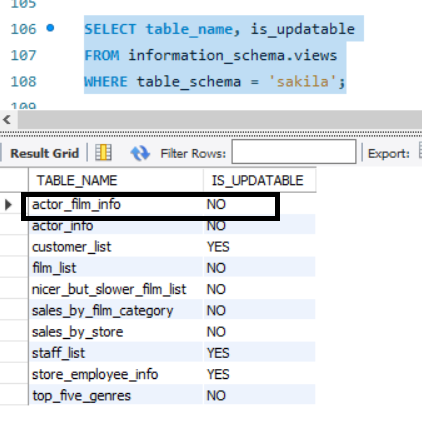
However, these views are not updatable. To check if a view is updatable or not, we can trigger the following query:
SELECT table_name, is_updatable
FROM information_schema.views
WHERE table_schema = 'sakila';
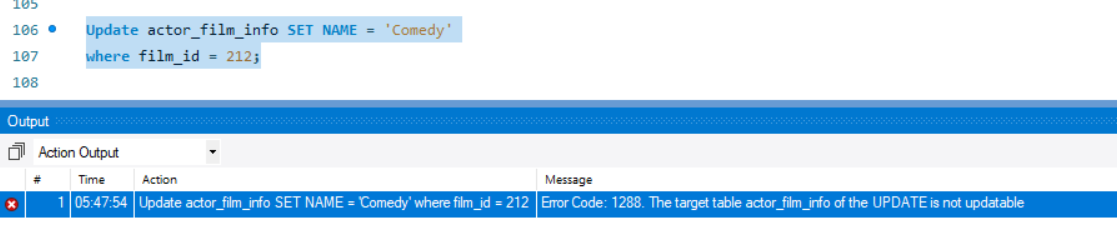
Updating such a view will result in an error.
Update actor_film_info SET NAME = 'Comedy'
where film_id = 212;
MySQL Create Updatable View
We can create updatable views as well in MySQL. However, to create such a view, the select query cannot have:
- Aggregate Functions
- Joins
- Distinct
- Group by and having clauses.
- Subqueries which refer to the outside query.
- Union or union all operators.
- Reference to other views which cannot be updated.
If any of these elements are present the created View is not updatable.
Example of an updatable view,
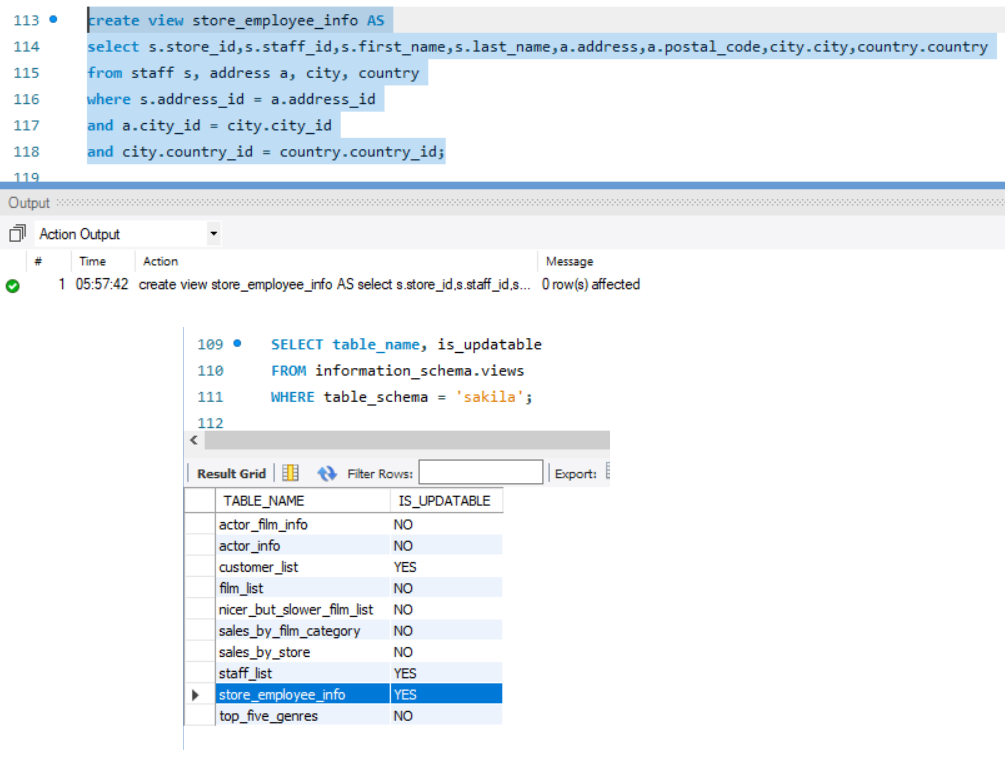
create view store_employee_info AS
select s.store_id,s.staff_id,s.first_name,s.last_name,a.address,a.postal_code,city.city,country.country
from staff s, address a, city, country
where s.address_id = a.address_id
and a.city_id = city.city_id
and city.country_id = country.country_id;
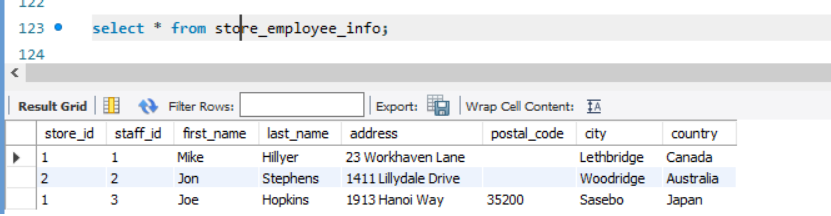
The records are:
Select * from store_employee_info;
Update a View in MySQL
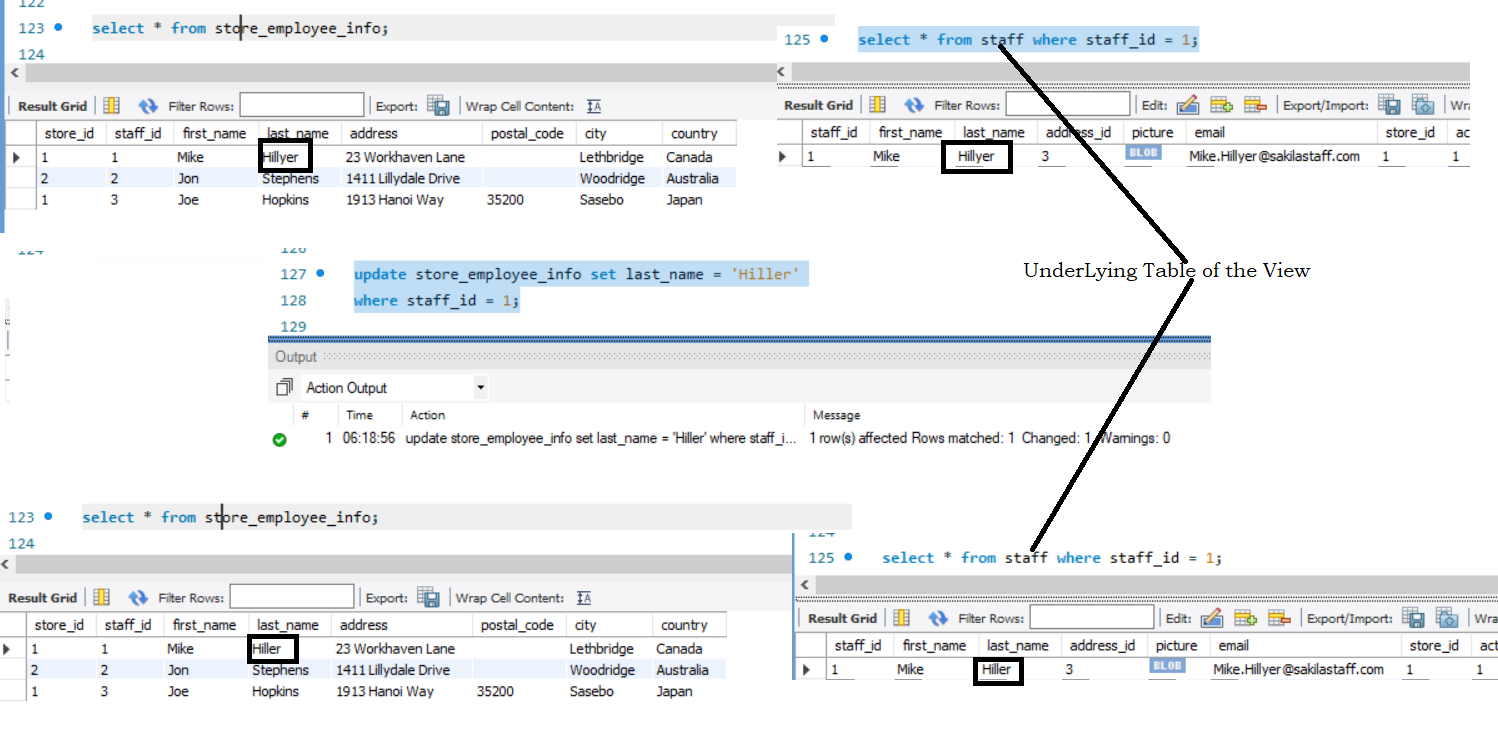
We can update updatable Views. Since Views are not physical tables, updating a View actually updates the underlying table.
update store_employee_info set last_name = 'Hiller'
where staff_id = 1;
This query actually goes and updates the underlying staff table. Hence it reflects in the View.
Drop a view in MySQL
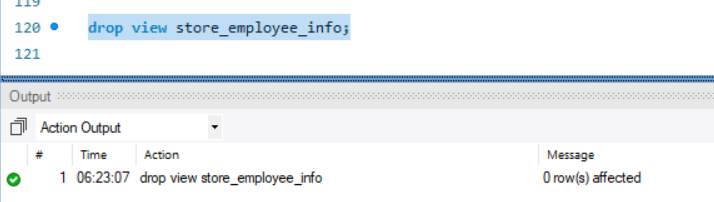
To drop a view we use the drop View statement. The Basic Syntax is
Drop View <view-name>;
Example:
Drop view staff_info;
Rename a View in MySQL
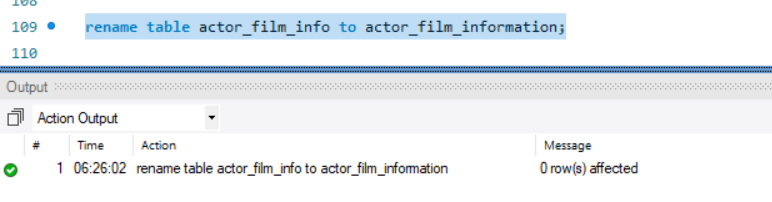
To rename a View we use the rename statement. The Basic syntax is
RENAME Table <table-name>;
example:
rename table actor_film_info to actor_film_information;
View creation Scripts,
To check the creation Script of the View, we can use the following query
Show create view <view-name>;
Example:
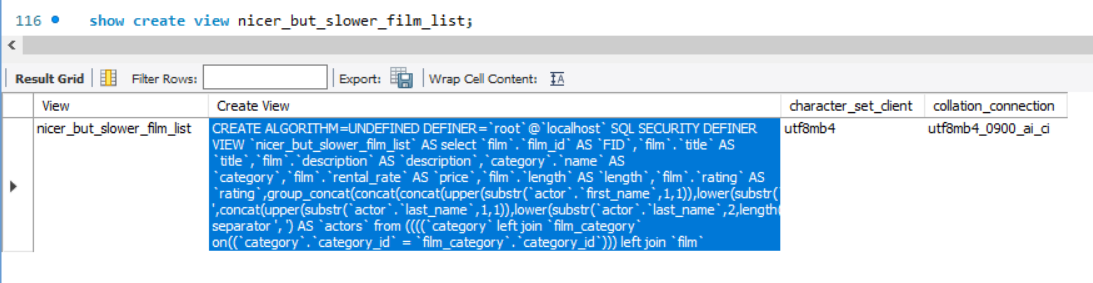
Show create view nicer_but_slower_film_list;